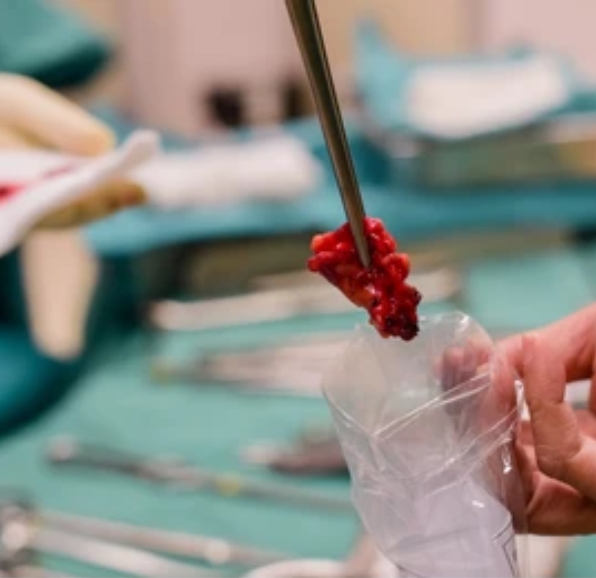
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is removed from the body for further examination under a microscope. It is commonly used to diagnose or rule out conditions such as cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases, providing a clear and definitive diagnosis for effective treatment planning.
Types of Biopsy Procedures
Needle Biopsy: This minimally invasive method uses a thin needle to extract tissue
or fluid from a lump or mass.
Core Needle Biopsy: A slightly larger needle is used to remove a core of tissue for
analysis.
Surgical Biopsy: In some cases, a small surgical procedure is required to remove a
sample or even the entire mass or lesion for testing.
Skin Biopsy: A sample of skin is taken to diagnose skin conditions like rashes,
infections, or skin cancers.
Most biopsies are minimally invasive, and the discomfort is usually brief and manageable. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area during needle biopsies, while surgical biopsies may require sedation or general anesthesia. After the procedure, some mild soreness may occur, but recovery is typically quick.